The following content is part of our Fly of the Month Club. This article is written by Peter Stitcher from Ascent Fly Fishing.


The grainy footage was captured on our family’s shoulder-mounted camcorder, technology so old that it’s probably coming back into style. Hopping next to a pond on that Smoky Mountain morning, a kid fills the frame as he struggles to hold onto his 10’ cane pole and what was surely the biggest catch of his young life. With a final heave, a confused and defeated rainbow trout was hoisted into the air and displayed to the camera. The pride and excitement of that moment echos through the years, and was the spark that lit my love for trout and passion for fishing. My guess is that this story may have resonated with many of you, bringing you back to the ponds and creeks of your youth and your first trout: the beloved and always eager rainbow trout.
In part III of our Trout Smart series, we will be breaking down a familiar friend, the most abundant of North American trout: Oncorhynchus mykiss, the Rainbow Trout.
Identifying Characteristics:
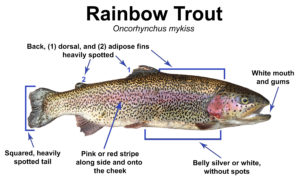

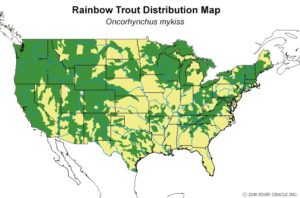
Range & Habitat:

Feeding Behavior and Foods:
Aquatic insects make up the lion’s share of the rainbow trout’s diet throughout its life. Midges, mayflies, caddisflies, and stoneflies each take their turn at the top of the menu, while terrestrial insects, minnows, and crayfish act more like appetizers and enter the diet of larger trout around age three. When looking at stomach samples of rainbow trout, it is common to find small bits of algae and aquatic plants which are consumed in the trout’s pursuit of sheltering invertebrates. Accused of thinking with their stomach more than their heads, rainbow trout feed with less caution than other species, and individual fish can often be hooked several times per day. When hooked, rainbow trout employ a couple of tactics. When your fly bites back, rainbows will often head for fast current, using their body like a parachute to harness the power of the river and apply maximum pressure to your leader. Their other trick is to go airborne, leaving the water like an ICBM launched from a submarine. This quick change in direction and explosive movement creates a quick, line-snapping force and has set more trout free than your state’s department of wildlife!
Vulnerabilities:
- They Think with Their Stomach – Given a decent approach & drift as well as some smarts in the matching-the-hatch department, you should be able to tempt almost any rainbow into snapping at your flies. With a short memory for the pain of previous hooks and an insatiable desire to feed, add a little flash in your fly patterns by using metal beads, wire wraps, or shiny material. Like a moth drawn to a flame, the rainbows in the river will give your fly a taste.
- Proven Responses for Predictable Tactics – Rainbow trout don’t have many moves when it comes to getting off the line, and the angler has a proven playbook for countering these moves. When the trout runs into current, drop your rod tip parallel with your bank and apply a steady, even pressure using the entire length of your rod. The added sting of this pressure will cause the rainbow to relent and work its way back to your bank and move upstream to lessen the bite of the hook. When the trout jumps, we momentarily release the pressure on our leader by dipping the tip of our rod to the water, before reestablishing a low rod and steady side-pressure once the trout reenters the water.
- They Like ‘Em Sunny-Side-Up – Like all trout, when there are fish eggs in the water, rainbows lose their little fishy minds! While not above poaching the eggs of other rainbows (Egg Puns!), they will also aggressively feed on sucker eggs in the spring, and brown or brook trout eggs in the fall. Eggs fill their dreams, so when the spawn is on, drop egg patterns!


